4 Economies Of Large Scale Production
-Differs from perfectly competitive markets where you have a large number of firms. Technical economies of scale.

On The Brink The Fourth Industrial Revolution What It Means And What To Do Industrial Revolution Fourth Industrial Revolution 4 Industrial Revolutions
They arise quite simple from an increase in the scale of production in the firm itself.

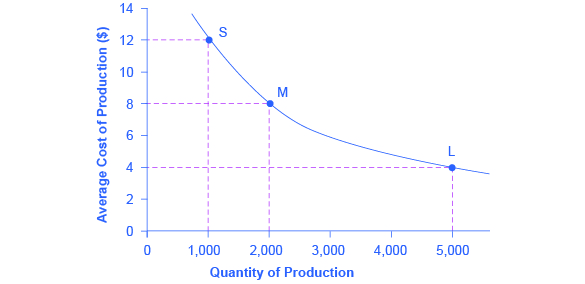
4 economies of large scale production. This may allow the larger firm to have a far lower unit cost such as 050 per loaf. They are not due to any increase in monopoly power or to any technological innovation. Specialisation of the workforce.
And the more businesses that came the more external economies of scale developed making it easier for more ventures to find facilities skilled labor suppliers sub-contractors and support. TAP THE CARD TO FLIP IT. Better transport electricity and communication facilities banking and insurance services.
Long-run marginal cost B. Classification of Large-Scale Production. Stories From A Southern Rural Law PracticeChris Callahan The Babe And The WolvesKempton Mooney.
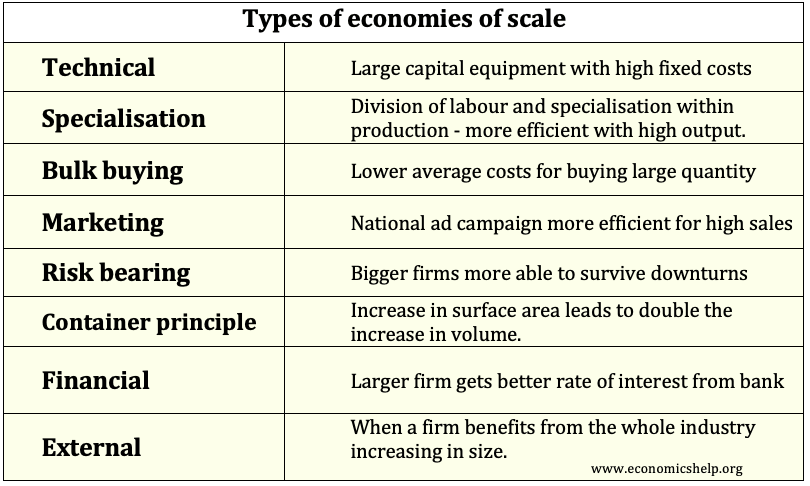
Different examples of how firms can benefit from economies of scale - specialisation bulk buying financial risk bearing technical and external economies of scale. External Economies Internal Economies of Scale. When a firm is reaping economies of large-scale production it experiences a fall in its.
They are open to a single factory. Marketing economies - from spreading the fixed cost of promotion over a larger level of output. It might not however be viable or cost-efficient for a small corner shop to buy this technology.
1 Internal Economies of Scale. -A market structure in which relatively few firms control all or most of the production and sale of a product. The economies of large scale production are classified by Marshall into.
Automated Production A volume production process involving machines controlled by production computers. The effect of economies of scale is to reduce the average unit costs of production. Purchasing economies - when large businesses often receive a discount because they are buying in bulk.
Internal economies of scale are those economies which are internal to the firm. Internal economies are internal to a firm when its costs of production are reduced and output increases. Long-run average cost C.
Long-run - Past Question and answers for schoolworks. 1 Internal Economies and 2 External Economies. That is larger businesses more readily have the cash and output to warrant buying materials in much larger quantities which can bring them per-unit cost advantages smaller businesses are otherwise unable to achieve.
This tends to benefit large firms. The economies of large scale production are classified by Marshall into 1. -In monopolies the products may be homogeneous or differentiated but the.
Second lower per-unit. Large-scale businesses can afford to invest in expensive and specialist capital machinery. These exist if the expansion in scale of the whole industry or group.
- When a firm is reaping economies of large-scale production it experiences a fall in its. The Economics Of Large Scale Production In British Industry. First specialization of labor and more integrated technology boost production volumes.
Economies of large scale production have been classified by Marshall into Internal Economies and External Economies. The advantages of large-scale production may be classified as External and Internal economies of production. Craft production A small-scale production process centred on manual skills.
Internal Economies and 2. There are several reasons why economies of scale give rise to lower per-unit costs. They are economies of scale achieved via buying in bulk.
A larger bakery that produces 500000 loaves a day can push suppliers for cheaper ingredients automate parts of the production process and produce larger batches. For example a supermarket chain such as Tesco or Sainsburys can invest in technology that improves stock control. Mechanized production A volume production process involving machines controlled by humans.
-Differs from monopolies because there is only one firm. For example a small bakery that produces 1000 loaves of bread a day may have a unit cost of 150. An Introductory StudyR A Guide To Preparing The History Curriculum In Primary Schools For An OFSTED Inspection Occasional PaperTim Lomas Bar Tales.
Economies which any single firm enjoys by virtue of its own individual policy is termed as Internal Economies. The small scale production secures all kinds of external economies which are available to large units also. Purchasing economies of scale also called buying economies of scale are a type of internal economy of scale.

Google Image Result For Https Www Researchgate Net Profile Alberto Zamprogna Publication 312975983 Figure Fig3 As 455191 Ecology Design Scale Insects Insects

Pakistanmovingforward In 2021 Moving Forward Growth Economy
Economies Of Scale Examples Economics Help

Main Types Of Economies In Production Distribution And Consumption The Geography Of Transport Systems Economy Learning Agricultural Development

Furfural Market Global Forecast To 2024 Marketsandmarkets Marketing Analysis Renewable Sources

Production Concept Basic Concepts Marketing Concept Integrated Activities

Eyecandy Infographic Portfolio Infographic You Sure Eye Candy

Fourth Industrial Revolution Technological Revolution Digital Revolution Industry 4 0 Png Digital Revolution Fourth Industrial Revolution Cyber Physical System

The Aluminium Unique Life Cycle Story Life Cycles Life Cycle Assessment Life

Eco 305 Week 3 Quiz 2 Chapters 3 And 4 All Possible Questions Chapter 3 Chapter Quiz
Economies Of Scale Definition Types Effects Of Economies Of Scale

What Are Economies Of Scale Economies Of Scale What Is Economy Economy

Pros And Cons Of Renewable Energy Renewable Energy Projects Renewable Energy Energy Projects
Economies Of Scale Microeconomics
Posting Komentar untuk "4 Economies Of Large Scale Production"