Economics J Curve Effect
North-Holland IS THERE A J-CURVE Andrew K. The above findings in the British economy can be explained by a phenomenon called the J- curve effect.
The J Curve effect shows what happens to the Balance of Payments when there is a depreciation.
Economics j curve effect. Journal of Monetary Economics 24 1989 53-68. The J-curve effect suggests that after a currency depreciation the current account balance will first fall for a period of time before beginning to rise as normally expected. Felmingham BS 1988 Where is the Australian J-curve.
We thus do not expect the J-curve effect to take place unless going forward the BOT bond issuance cut is large enough to result in the falling outstanding. If the value of balance of trade is positive that is if the balance of trade lies above the zero line and the curve rises the balance of trade improves. First the J-Curve is influenced by the level of fees early on in the funds life.
The J-curve in international trade describes the effects on imports and exports of the depreciation of a countrys currency. Bulletin of Economic Research 40 4356. But eventually the currency devaluation reduces the price of its exports.
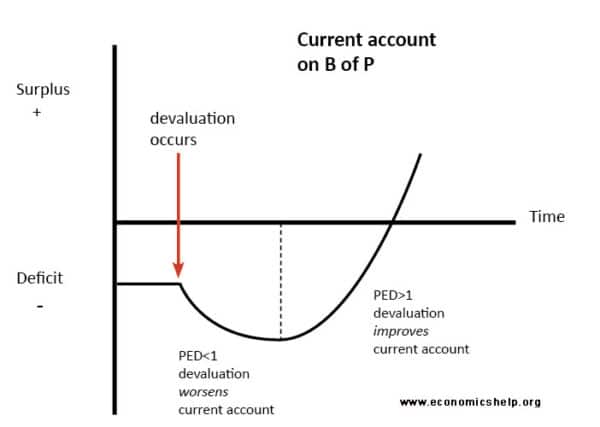
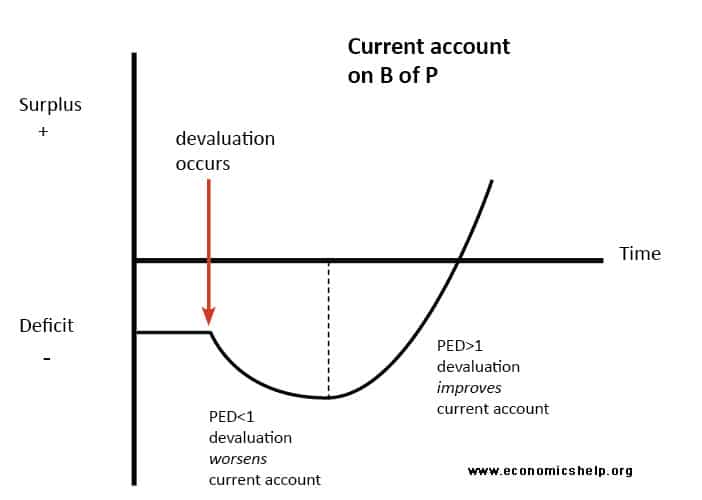
It is expected that a rise in the exchange rate of a currency against another will lead to an improved trade balance. The J Curve effect shows the possible time lags between a falling currency and an improved trade balance. Unfortunately in the short-run products are inelastic because of an information lag.
In this short revision video we explain the reasoning behind the J Curve effect and the importance of the Marshall Lerner condition and price elasticities of demand for imports an exports. As depreciation makes imports more expensive and exports cheaper both in terms of the buyers currency it should increase exports and decrease imports. Quarterly Review of Economics and Finance 52 1537.
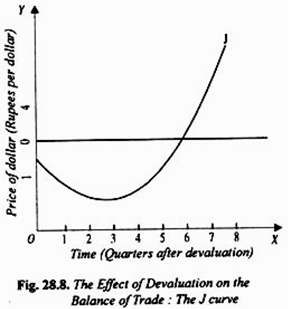
This J-curve effect is shown in Fig. Marshall Lerner Condition and J Curve Effect - An in depth look at the Marshall Lerner condition and J curve effect in determining whether a fall in the exch. If a country has a trade deficit initially the deficit will first rise and then fall in response to a currency depreciation.
Crossref ISI Google Scholar. This can be split into both short and long run. Initially a countrys external trade deficit The effect of currency depreciation on the trade deficit depends on price elasticity of demand for exports imports.
If a country decides to devalue its currency in order to become more competitive in the international market the revenue from exports will only increase if the exports are elastic and if imports are also elastic. The effect of the depreciation is a fall in. J Curve in Economics.
From the Marshall Lerner condition if the elasticities of exports and imports are more than 1 a depreciation would lead to an improvement in the balance of payments. Applied Economics 31 687395. A countrys trade balance experiences the J-curve effect if its currency becomes devalued.
This refers to a phenomenon wherein the trade balance of a country worsens following the depreciation of. A weak currency means that imports will be costly while it will be more profitable to export commodities. Among the 3 factors leading to the J-curve effect we believe the first 2 factors are panning out.
In economics a J Curve refers to a change in the countrys balance of trade often following a currency devaluation or depreciation. Since the Indonesian economy has been hit by a crisis starting with a foreign exchange depreciation to almost all of the currency in the world particularly US and the components of net exports are exports and imports therefore Indonesian currency rupiah. The J-curve effect is often cited in economics to describe for instance the way that a countrys balance of trade initially worsens following a devaluation of its currency then quickly.
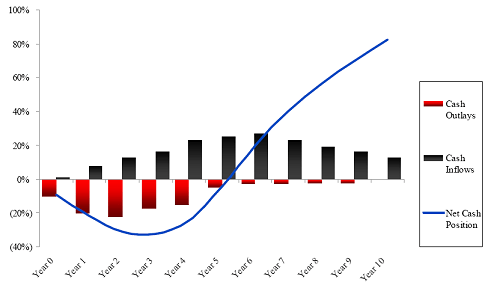
Since management fees are based on the entire committed capital while this capital is only gradually invested over the first few years and distributions are usually miniscule management fees and organisational expenses have a significant effect on the shape of the J-Curve. BOT bond issuance comparison between April 2017 and July 2019. The research is about factors influencing Indonesian net exports condition and the existence of a J curve effect.
But the third factor is not. Explaining the J Curve. YELLEN University of California Berkeley CA 94720 USA Received June 1987 final version received April 1988 If the response of the value of the trade balance to movements in the real exchange rate is described by a J-curve then a real.
At first the countrys total value of imports goods purchased from abroad exceeds its total value of exports goods sold abroad resulting in a trade deficit. ROSE and Janet L. Doroodian K C Jung and R Boyd 1999 The J-curve effect and US agricultural and industrial trade.
What is J-curve effect in Economics. AQA Edexcel OCR IB Eduqas WJEC. 358 where along the X-axis we measure time that is quarters after devaluation and on the Y-axis we measure the balance of trade.

Econknowhow The J Curve Effect

J Curve Effect Definition Example Investinganswers

Effect Of Exchange Rate On International Trade Unbrick Id

J Curve Meaning Concept And How It Works Penpoin
Ppt The J Curve Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 1612334

J Curve Private Equity Youtube

The J Curve Impact Of Exchange Rate Changes On National Economies Finance Train

J Curve And The Marshall Lerner Condition Youtube
Effects Of Depreciation And Devaluation Of The Exchange Rate
J Curve Understanding How J Curve Works In Pe And Economics

Econ By Reyrey Marshall Lerner Condition J Curve


Posting Komentar untuk "Economics J Curve Effect"