Economics Provides Short And Long Run Plant Capacity Size
Total Fixed cost as the name implies is the cost of the firms fixed resources Fixed cost remains the same in the short run. The simple meaning of economies of scale is doing things more efficiently with increasing size.
Pipes And Pipe Sizing Spirax Sarco
In figure 62 the equilibrium of the monopolist is defined by point ɛ at which the MC intersects the.
Economics provides short and long run plant capacity size. There is no reserve. A factor of production whose quantity can be changed during a particular period is a. Short-run and long-run and arrives at the conclusion that both the short.
Diseconomies of scale exist when long-run average cost LRAC increase as output along with the plant size enlarges. Long enough in which to make all economic adjustments. The short run is a period that is.
The total cost of a firm in the short run is divided into two categories 1 Fixed cost and 2 Variable cost. It cannot in the short-run enlarge the size of the existing plant or build a new plant of a bigger capacity. The third layer concerning the determination of the most profitable size and equipment of plant relates to what is called long-run profit maximization.
Less than one week. Secondly the slope of MC is greater than the slope of the MR at the point of intersection. As a larger input buyer the firm can purchase inputs at a lower per unit cost.
The two types of economic costs are now discussed in brief. Economies of scale exist as a firm increases its size in the long run because of all of the following except Select one. In the short run a firm can operate on any SAC given the size of the plant.
In economics the long-run is a theoretical concept in which all markets are in equilibrium and all prices and quantities have fully adjusted and are in equilibrium. Similarly when demand falls the firm would reduce the work hours or output but cannot downsize its plant. In the short run the firm can operate on any short -run average cost curve given the size of the plant.
Below are the short-run average-total-cost schedules for three plants of different size that a firm might build to produce its product. The firm can afford more sophisticated technology in production. In the long run plant capacity and the number of firms can change.
Thus in the short-run only variable factors can be varied while the fixed factors remain the same. This cost ative disadvantage of large scale when the firm size expand beyond the optimal size. Less than one month.
The shape of the long-run total cost curve is S-shaped much similar to a short-run total cost curve. The short-run marginal cost measures the cost to produce a unit of electric energy not power given an existing power plant. Decreases as plant size increases due to the economies of scale which the.
In the long-run we want to select a plant size that gives us the lowest costs for our level of output. B In the long run what plant size should the firm build if it wants to produce. The long run marginal cost measures the cost to produce a unit of electric energy where we dont assume that the capacity of the plant is fixed.
On the other hand long-run is a period of time during which the quantities of all factors variable as well as fixed can be adjusted. Total fixed cost occur only in the short run. For relatively small quantities of output the slope begins to flatten.
A plant with a 500 tday capacity is much more flexible than one with a 250 tday capacity but the costs of a 250 t plant are not very different from a 500 tday plant. Minimization of short-run costs The production function. The plant size due to labor specialization applying better technology l advantages and also through learning economies.
1 Total Fixed Cost TFC. The figure depicts the long-run total cost curve of a firm. CategoriesTypes of Costs in the Short Run.
If a firm intends to increase its output in the short run it would need to hire more workers and purchase more raw materialsThe firm cannot expand its plant size or increase the plant capacity in the short run. The long-run contrasts with the short-run in which there are some constraints and markets are not fully in equilibrium. While firms have some ability to adjust output in the short run they have a greater ability to adjust in the long-run.
If the desired output is only 25 units then a small plant is able to produce at a lower average cost 40 than the medium size plant 50. Long enough in which to vary output but not plant capacity. When a firm expands its size to the lowest point of the long-run average cost LAC it sets up a plant which given the state of technology has the lowest unit cost of production when operated at its full capacity.
These SACs are also called plant curves. This is illustrated with an elastic supply curve. Then for larger quantities the slope makes a turn-around and becomes steeper.
The monopolist maximizes his short-run profits if the following two conditions are fulfilled Firstly the MC is equal to the MR. Labor and management can specialize even further in their tasks. Variable factor of production.
More specifically in microeconomics there are no fixed factors of production in the long-run and. Assume that these are the only possible sizes of plants that the firm might build. So the short run marginal cost captures fuel and variable OM costs.
For example lets assume we can build different sizes of a plant. For the sake of our understanding lets assume that there are only three plants that are technically possible. In case the volume of sales expands to 400 units the size of the plant will be increased and the desired output will be attained by the scale of plant represented by SAC 2 at point B If the anticipated output rate is 600 units the firm will build the size of plant given by SAC 3 and operate it at point C where the average cost is 26 and also the lowest The optimum output of the firm is obtained at point C on the medium size plant.
However much of a commodity a business firm produces it endeavours to produce it as cheaply as possible. To understand the derivation of a long run average cost curve lets consider three short run average cost curves SACs as shown in Fig. Building an oversized plant is a safety measure so that when trawlers supply up to 90 tday during periods of high catches it can be processed during the course of the day.
As far as the long run is concerned the firm can take the liberty of determining which size of plant or on which short-run average curve should the firm operate in order to produce a given level of output at the minimum possible cost. As has been explained above that long-run average cost of a firm is influenced by the various economies and diseconomies of scale. Common sources of economies of scale are purchasing bulk buying of materials through long-term contracts managerial increasing the specialization of managers financial obtaining lower-interest charges when borrowing from banks and having access to a greater.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)
Minimum Efficient Scale Mes Definition

Wind Energy Turbines Are Getting Taller Bigger And More Powerful Vox
The Common Size Analysis Of Financial Statements
Sustainability Free Full Text Small And Medium Sized Enterprises Smes The Engine Of Economic Growth Through Investments And Innovation Html

Campervan Sizes And Types Vanlife Adventure

Yamaha Sight Price In Philippines Yamaha Fuel Injection Cylinder Head

Tesla Model 3 Gets Official Epa Rating Of 310 Miles And 126 Mpge Tesla Model Tesla Electric Charging Stations
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/10382023/Wind_turbine_heights.jpg)
Wind Energy Turbines Are Getting Taller Bigger And More Powerful Vox

Yamaha Mio I 125 Yamaha Vibrant Orange Black N Yellow
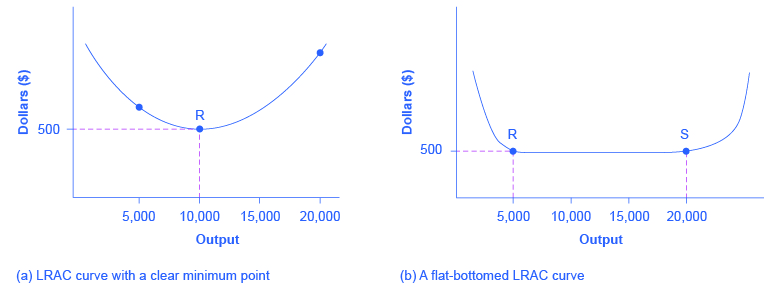
7 3 The Structure Of Costs In The Long Run Principles Of Economics
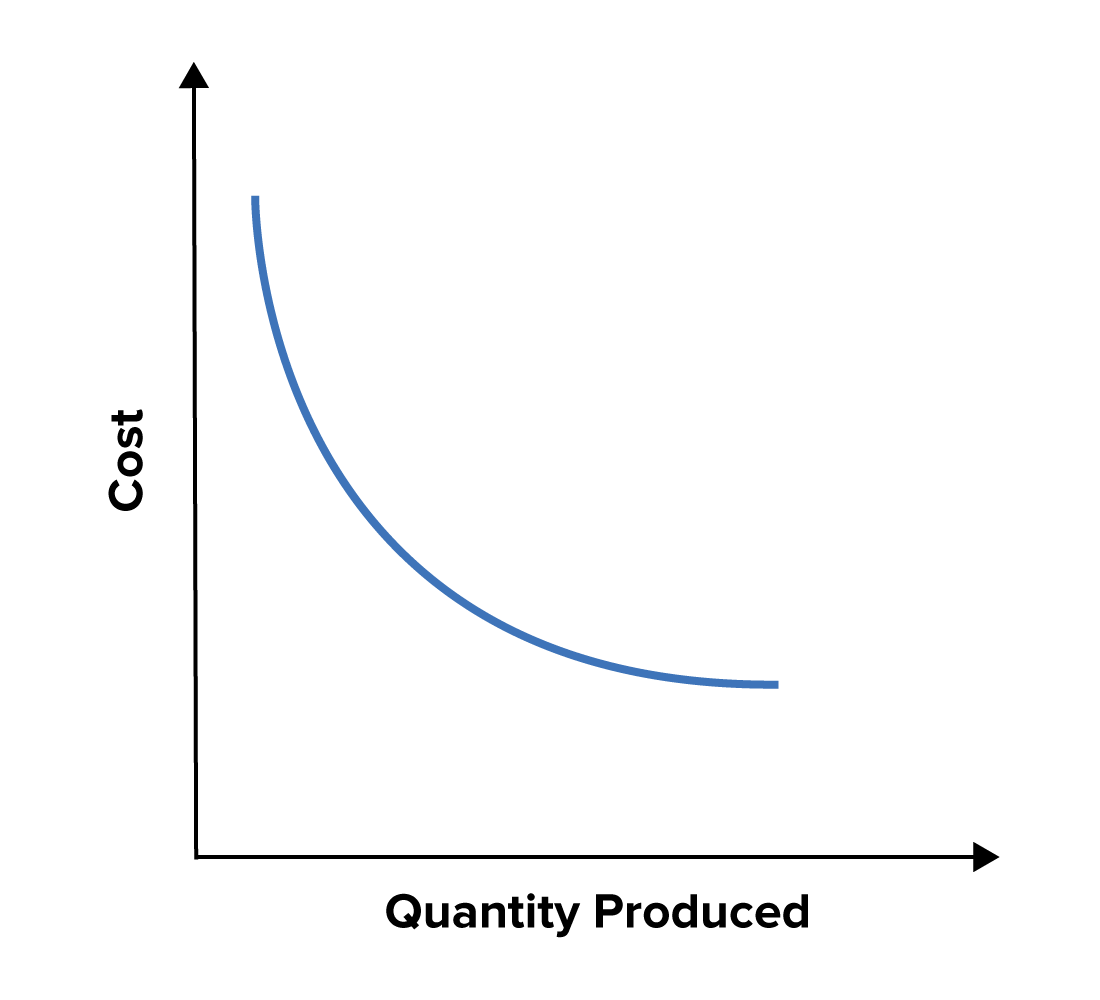
Achieving Economies Of Scale Strategy Tools From Mindtools Com
Population Ecology Biology For Majors Ii

How Individuals Engage In The Absorption Of New External Knowledge A Process Model Of Absorptive Capacity Sjodin 2019 Journal Of Product Innovation Management Wiley Online Library

Posting Komentar untuk "Economics Provides Short And Long Run Plant Capacity Size"