Economics Equilibrium
Economic equilibrium refers to a situation wherein specific market forces remain in balance resulting in optimal market conditions in a market-based economy. The equilibrium price is a meeting point between supply and demand.
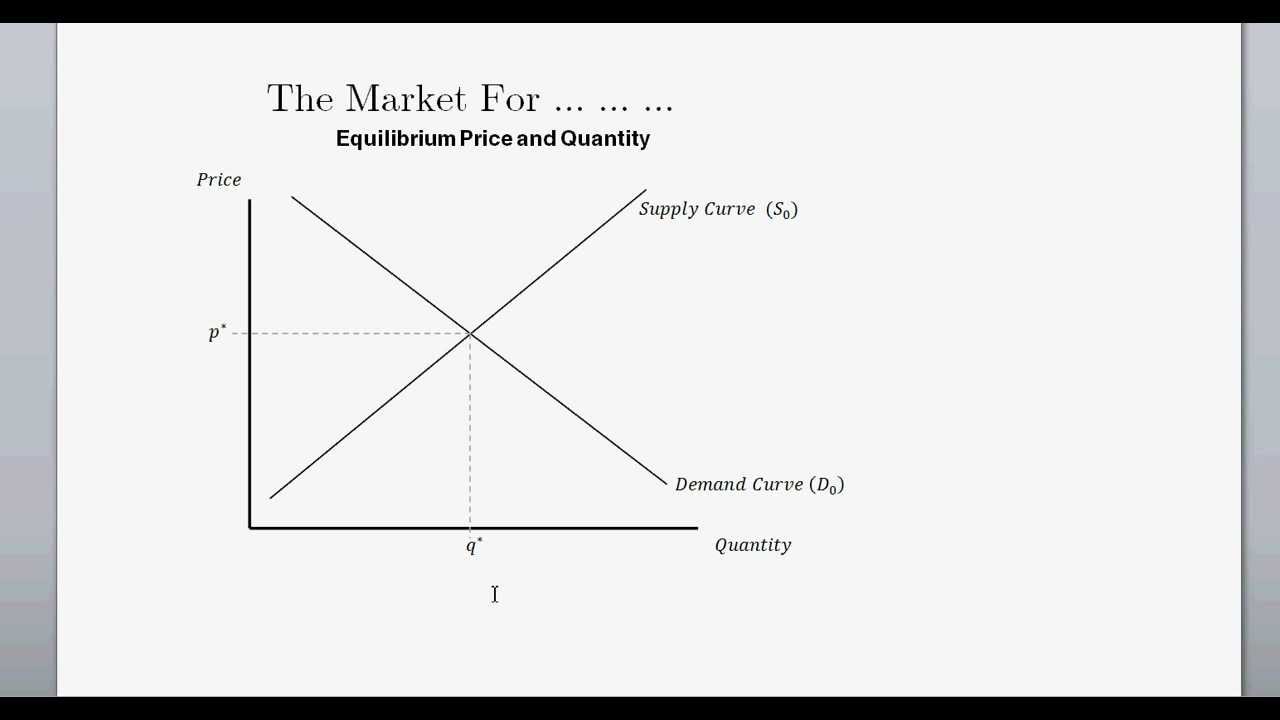
Supply And Demand And Equilibrium Price Quanitity Intro To Microeconomics Youtube Teaching Economics Equilibrium Economics
Since then the concept has come under sustained attack from all points of the heterodox compass from Austrian economists to Marxists.

Economics equilibrium. The equilibrium price of a good or service therefore is its price when the. When the supply and demand curves intersect the market is in equilibrium. In an open economy equilibrium is achieved when supply and demand are balanced.
22 General Equilibrium In economics general equilibrium theory attempts to explain the behavior of supply demand and prices in a whole economy with several or many interacting markets by seeking to prove that the interaction of demand and supply will result in an overall or general equilibrium. Both parties require the scarce resource that the other has and hence there is a considerable incentive to engage in an exchange. Economic theory suggests that in a free market there will be a single price which brings demand and supply into balance called equilibrium price.
Partly in response to these pressures mainstream. If an economy is a complex system behavior is resulting as collectively generated from the actions of individual agents. In economics economic equilibrium is a situation in which economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the equilibrium values of economic variables will not change.
The market is pictured as a sort of analogue computer solving this system of inequalities. The term is often used to describe the balance between supply and demand or in other words the perfect relationship between buyers and sellers. At a price below the equilibrium there is.
Because agent behaviors interact in nonlinear ways the collective behavior result that emerges can have a life of its. The equilibrium quantity is the quantity demanded and supplied at the equilibrium price. Economic equilibrium is a condition or state in which economic forces are balanced.
How do we attain equilibrium. In the case of market equilibrium in an open economy equilibrium occurs when a market price is established through competition. Economists use the term equilibrium to describe the balance between supply and demand in the marketplace.
The equilibrium price is the price that equals the quantity offered and the quantity demanded of an economic good on the market. In economics general equilibrium theory attempts to explain the behavior of supply demand and prices in a whole economy with several or many interacting markets by seeking to prove that the interaction of demand and supply will result in an overall general equilibrium. This is with the absence of external forces and the values of these economic variables do not change.
General equilibrium theory contrasts to the theory of partial equilibrium. In economics equilibrium is an economic state whereby there exists a balance between economic forces such as demand and supply. General Equilibrium Theory which became the dominating paradigm after the Second World War is founded on the postulated existence uniqueness and stability of equilibrium in economic processes.
A complex system differs in important ways from the general equilibrium system of neoclassical economics. We start by deriving the demand curve and describe the characteristics of demand. Finally we explore what happens when demand and supply interact and what happens when market conditions change.
An equilibrium is usually defined as a price vector p and an associated collection of individual demands and supplies such that. 49 rows Definition of market equilibrium A situation where for a particular good. When no external influences are present the state of equilibrium between the variables will not change.
At a price above the equilibrium there is a natural tendency for the price to fall. Zp 0 and pt ZkP 0 for k I. Market equilibrium occurs when market supply equals market demand.
On the other hand a market characterized by a scarcity of demand and a high supply has a very low equilibrium price. Next we describe the characteristics of supply. Equilibrium is vulnerable to both internal and external influences.
The equilibrium price in the market for coffee is thus 6 per pound. In this unit we explore markets which is any interaction between buyers and sellers. Under ideal market conditions price tends to settle within a stable range when output satisfies customer demand for that good or service.

Market Equilibrium Explained Economics Lessons Economics Notes Microeconomics Study

Guide To The Supply And Demand Equilibrium Economics Lessons Economy Lessons Macroeconomics

Diagram Showing The Demand And Supply Curves The Market Equilibrium And A Surplus And A Shortage Teaching Economics Economics Notes Microeconomics Study

Changes In Economic Equilibrium

Defying The Laws Of Economics An Exercise In Futility Or Evidence Of Insanity Economics Lessons Basic Economics Economics

Supply And Demand Economics Economic Science Microeconomics Study

Equilibrium And Its Adjustment Economics Notes Study Materials Ma Economics

How To Calculate An Equilibrium Equation In Economics Equilibrium Calculator Economics

Equilibrium Price Learning Math Equilibrium Economics

Are You At Equilibrium Supply Demand Curve Econ Trivet Zazzle Com In 2021 Equilibrium Curve Economics Humor

Understanding Market Equilibrium Economics Understanding Equilibrium

Supply Meets Demand Economics Lesson Distance Learning Economics Lessons High School Lesson Plans Economics

Guide To The Supply And Demand Equilibrium Equilibrium Macroeconomics Saving For College

Changes In Economic Equilibrium Equilibrium Economics Syllabus
Posting Komentar untuk "Economics Equilibrium"