Economics J Curve
Updated November 4 2020. The main article for this category is Economic.
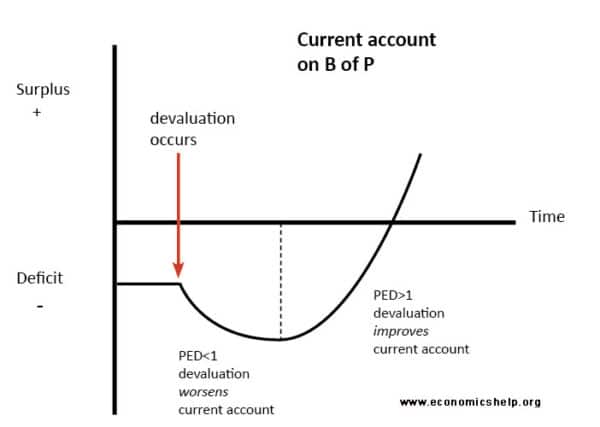
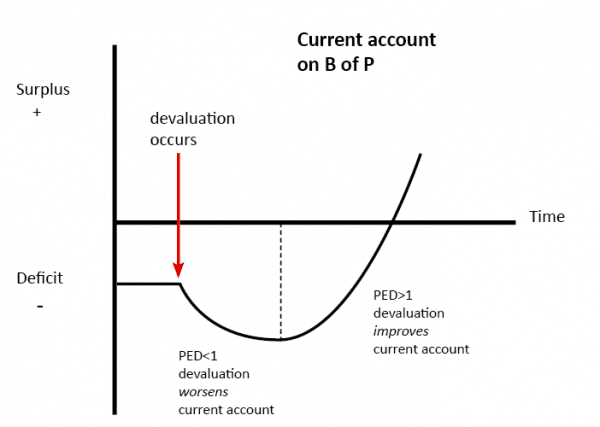
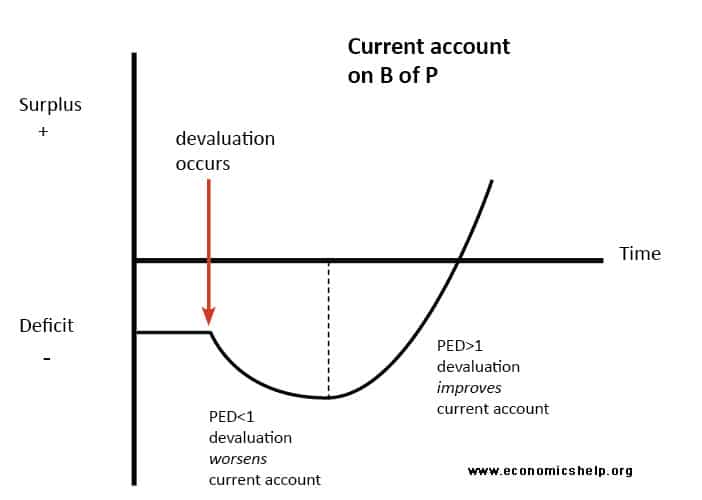
The J Curve effect shows the possible time lags between a falling currency and an improved trade balance.

Economics j curve. Evidence from East Asia 401 price of imports will result in a decrease in the quantity demanded of imports. Estimating this partial derivative in both the long and short run is the primary objective of this paper. A weak currency means that imports will be costly while it will be more profitable to export commodities.
If certain restrictions on demand and supply of imports and exports are met3 a depreciation of a currency will lead to an increase in the value of exports and a. 4 Their J-curve describes how trade balances react over time to changes in real exchange rates. A weak currency means that imports will be costly while it will be more profitable to export commodities.
The J-curve theory represents a short-term exception to the standard assumption applied in the GS model in which a currency depreciation causes a decrease in the trade deficit. The Jcurve hypothesis has gained relevance since the end of the Bretton Woods System in 1973 Kulkarni and Clarke 2009. 5 The similarity between the two J-.
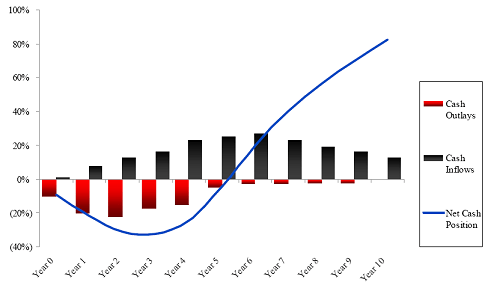
How Does a J Curve Work. First the J-Curve is influenced by the level of fees early on in the funds life. The effect of currency depreciation on the trade deficit depends on price elasticity of demand for exports.
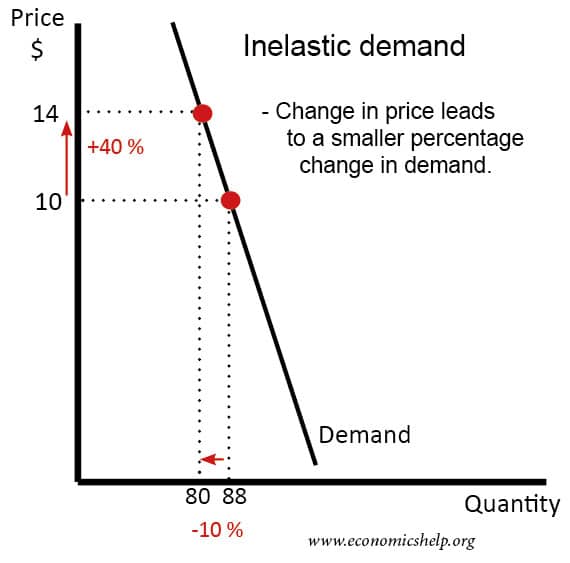
What is a J Curve. The J curve represents a hypothetical short-term increase in a countrys trade deficit that occurs immediately following a decline in the value of its currency. In this short revision video we explain the reasoning behind the J Curve effect and the importance of the Marshall Lerner condition and price elasticities of demand for imports an exports.
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia. Political scientist Ian Bremmers latest book The J Curve has stirred up a welcome. J-curve ˈdʒeɪ kɜːv-kɜːrv noun countable ECONOMICS.
A countrys trade balance experiences the J-curve effect if its currency becomes devalued. Initially a countrys external trade deficit X-M might increase following a currency depreciation. Jump to navigation Jump to search.
A J-curve is defined as the combination of a negative short-run derivative with a. AQA Edexcel OCR IB Eduqas WJEC. Wikimedia Commons has media related to Economic curves.
Explaining the J Curve. Since management fees are based on the entire committed capital while this capital is only gradually invested over the first few years and distributions are usually miniscule. At first the countrys total value of imports goods purchased from abroad exceeds its total value of exports goods sold abroad resulting in a trade deficit.
The Productivity J-Curve that we describe in this paper is related to but distinct from the trade balance J-curve of Magee 1973 and Rose and Yellen 1989. In economics a J Curve refers to a change in the countrys balance of trade often following a currency devaluation or depreciation. The work of Magee 1973 is believed to be the first work on testing the J-curve hypothesis in the international economics literature Bahmani-Oskooee and Goswami 2003.
The shape of the J-Curve The depth and length of a J-Curve depends on several factors. It also shows the link between microeconomic principles elasticity and macroeconomic outcomes current account The current account on the balance of payments measures the net value X-M of exports and imports of goods services and investment incomes. The J-Curve is an example of how time lags can affect economic policy.
A line on a GRAPH in the shape of a letter J which represents a slight fall in the level of something followed by an increase Analysts are talking about a J-curve effect with a slight downturn in share prices followed by a recovery later. Economics also affects the J curve. The theory of the J-curve is an explanation for the J-like temporal pattern of change in a countrys trade balance in response to a sudden or substantial depreciation or devaluation of the currency.
A weak economy is more susceptible to deeper faster shocks because it lacks the ability to rebuild infrastructure or restore external trade. In economics a J Curve refers to a change in the countrys balance of trade often following a currency devaluation or depreciation. A theoretical argument for development not democracy in Iraq.
But eventually the currency devaluation reduces the price of its exports. The J-curve effect is often cited in economics to describe for instance the way that a countrys balance of trade initially worsens following a devaluation of its currency then quickly.

Balance Of Payments Problems And Policies Economics Online Economics Online
.jpg)
Important Economic Curves For Upsc

Rostow S Stages Of Economic Growth Represented On An X Y Graph Download Scientific Diagram

J Curve And The Marshall Lerner Condition Youtube
J Curve Understanding How J Curve Works In Pe And Economics

J Curve And The Marshall Lerner Condition Youtube

J Curve Effect Definition Example Investinganswers

J Curve Meaning Concept And How It Works Penpoin
Posting Komentar untuk "Economics J Curve"